Officials and health authorities in the southern Indian state of Kerala are actively engaged in efforts to control and mitigate a fresh outbreak of the Nipah virus, a highly contagious and potentially lethal pathogen. As part of their containment strategy, the state government has implemented a comprehensive plan to establish a significant containment zone around the precise location where the outbreak initially occurred. This zone has been meticulously demarcated and securely cordoned off to prevent the virus from spreading further into unaffected areas.
The swift and decisive action taken by the authorities underscores the seriousness with which they are addressing this public health threat. By creating this containment zone, they aim to limit the virus’s transmission and safeguard the health of the population, implementing stringent measures to isolate and treat infected individuals while conducting rigorous contact tracing to identify potential cases. This proactive approach is crucial in not only stemming the current outbreak but also in preventing any potential wider spread of the Nipah virus, thereby protecting the health and well-being of the broader community.
Health authorities are actively engaged in the critical task of identifying and isolating individuals who have had close contact with those infected by the Nipah virus. Concurrently, residents in neighboring regions have been promptly alerted to remain vigilant and take necessary precautions.
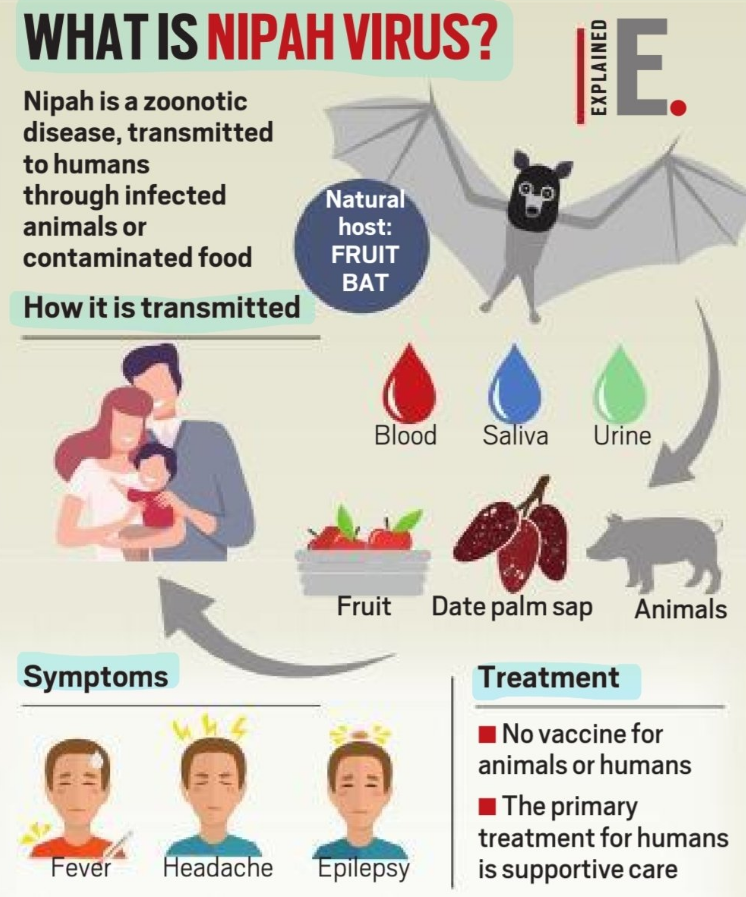
This particular strain of the virus is suspected to be a variant initially identified in Bangladesh. It’s important to note that both humans and animals can transmit the virus to each other, either directly through respiratory droplets or contact with contaminated surfaces. Furthermore, human-to-human transmission is also a significant concern, underscoring the need for strict preventive measures to curtail its spread.
This infection can result in encephalitis, ranging from mild to severe illness, and in some cases, it can even be fatal. Notably, in the variant initially identified in Bangladesh, the mortality rate is alarmingly high, with one-third of patients succumbing to the virus. It’s worth mentioning that despite its high fatality rate, this particular variant is generally regarded as less contagious compared to other strains.
What are the Treatment Options for this Disease?
Currently, there is no available vaccine or specific medication for either animals or humans to combat the Nipah virus. Medical treatments have, at best, been able to alleviate the symptoms associated with the infection.
In practice, it is imperative to promptly isolate infected patients and provide them with intensive care in specialized units capable of supporting vital bodily functions.
To effectively halt the transmission of this infectious disease, individuals who have been in contact with confirmed cases or are suspected of having the virus must undergo quarantine measures. These precautions are crucial in preventing the further spread of the disease within the community.